Demystifying UX and UI: Understanding Their Unique Roles
Exploring the Interplay Between User Experience and User Interface Design
In digital product design, two terms often arise in conversation: UX (User Experience) and UI (User Interface). While both are integral to creating compelling digital experiences, they serve distinct roles and contribute uniquely to the overall design process. Let's delve into the differences between UX and UI, exploring their characteristics and understanding how they intersect to shape user interactions.
User Experience (UX):
User Experience design focuses on the holistic experience of interacting with a digital product, encompassing the user's journey from initial discovery to task completion. UX designers are concerned with understanding user needs, behaviours, and motivations and crafting solutions that effectively address these needs. It involves research, wireframing, prototyping, and testing to ensure a seamless and intuitive user experience.
Key Elements of UX Design:
User Research: Understanding users’ needs, goals, and pain points through qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Information Architecture: Organizing and structuring content in a way that is logical and intuitive for users to navigate.
Wireframing and Prototyping: Creating low-fidelity wireframes and interactive prototypes to visualize the user flow and test design concepts.
Usability Testing: Gathering user feedback (VoC) to identify usability issues and iteratively improve the design based on their insights.
User Interface (UI):
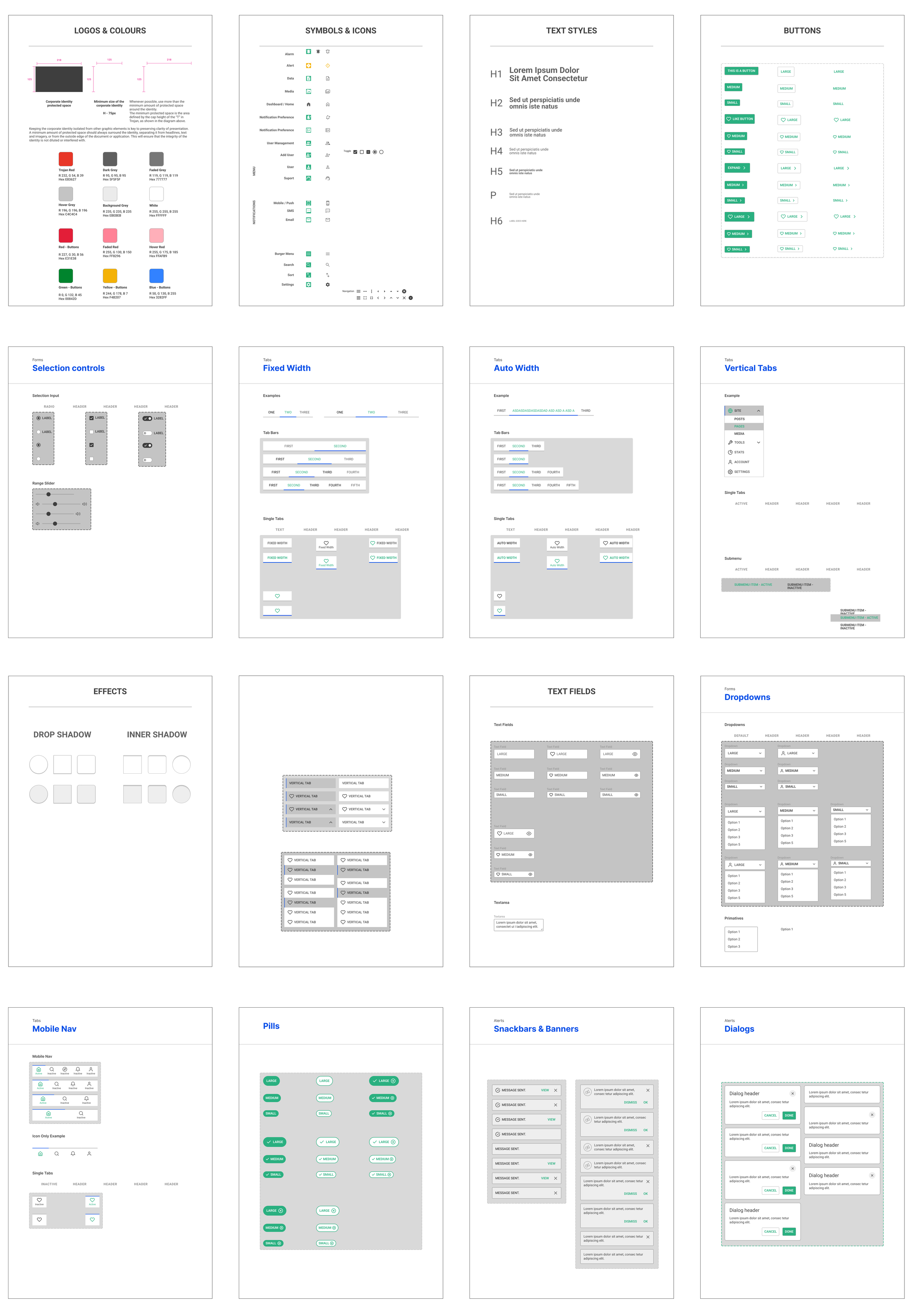
User Interface design focuses on a digital product's visual and interactive elements, including layouts, typography, colours, and interactive components. UI designers are responsible for creating visually appealing interfaces that communicate the brand's identity and guide users through their interactions. It involves creating style guides, designing interface elements, and collaborating closely with UX designers to ensure consistency and coherence in the overall design.
Key Elements of UI Design:
Visual Design: Creating visually appealing interfaces that reflect the brand's identity and evoke the desired emotional response from users.
Typography and Color: Selecting appropriate fonts and colour palettes to enhance readability, usability, and aesthetic appeal.
Interactive Design: Designing interactive elements like buttons, forms, and animations to facilitate user interactions and provide feedback.
Design Systems: Developing and maintaining design systems and style guides to ensure consistency and scalability across all touchpoints.
Interplay Between UX and UI:
While UX and UI design are often discussed separately, they are inherently interconnected and complement each other in creating exceptional digital experiences. UX lays the foundation for a user-centred design process, focusing on understanding user needs and designing intuitive interactions, while UI brings those interactions to life through visually compelling interfaces.
It's important to recognize that one may become more relevant depending on a project's application, use cases, and requirements. A strong emphasis on UX design may sometimes be necessary to streamline complex workflows and prioritize functionality. In contrast, in others, a polished UI design may be the key to capturing users' attention and fostering brand engagement.
In conclusion, UX and UI design are essential to creating successful digital experiences. By understanding the differences between the two and leveraging their strengths based on project requirements, designers can craft intuitive, visually appealing interfaces that resonate with users and drive business objectives.